-
01-01-1940: King George VI of Great Britain signs a decree introducing compulsory military service for all men between the ages 19 and 28.
-
02-01-1940: Finland reports having encircled 55,000 Soviet troops on her eastern border.
-
02-01-1940: The Dutch government issues new instructions to the supreme commander of all armed forces, General Reijnders, pertaining to the defense of Fortress Holland and the Grebbe line. He protests.
-
03-01-1940: Feldmarschall Hermann Göring is charged with responsibility for the German war economy.
-
05-01-1940: East of Soumussalmi, the Finnish 9th Division destroys the Soviet 44th Raider Regiment.
-
05-01-1940: The British warn Norway, the Royal Navy will enter her territorial waters in case the Norwegians allow German vessels to be loaded illegally with iron ore.
-
05-01-1940: The British Secretary of Defense Hore-Belisha is replaced by Oliver Stanley.
-
06-01-1940: The Dutch government announces negotiations about the Dutch neutrality are out of the question.
-
07-01-1940: The Dutch government rejects most of the objections made by General Reijnders pertaining to the instructions of January 2, 1940.
-
08-01-1940: Food rationing is introduced in Great Britain.
-
09-01-1940: Both China and Japan claim to have won the battle for the province of Gwangdong in the north.
-
10-01-1940: Two German Luftwaffe officers make an emergency landing near Malines on the river Meuse in Belgium. It transpires they are carrying plans for a German offensive against the Netherlands and Belgium; these plans wind up in Belgian hands.
-
10-01-1940: Hitler sets the date for Fall Gelb at January 17, 1940.
-
11-01-1940: Food rationing is introduced in France.
-
12-01-1940: Soviet aircraft bomb the Finnish cities of Turku, Lahti and Helsinki.
-
13-01-1940: The Netherlands and Belgium put their armed forces on full alert.
-
14-01-1940: The Soviet Union lodges complaints with Sweden and Norway for supporting Finland.
-
14-01-1940: In the Netherlands, periodic leave is temporarily suspended.
-
15-01-1940: The Belgian government rejects the proposal to grant Allied troops access to Belgian territory.
-
15-01-1940: Reports state Japanese troops in China are withdrawing to Gwangdzjow (Canton) in the province of Gwangdong.
-
15-01-1940: General Reijnders submits his objections against the war policy of the Dutch government in writing.
-
16-01-1940: Hitler orders a postponement of the attack on the Netherlands, Belgium and France scheduled for January.
-
16-01-1940: The Allies plan a military action in Norway.
-
18-01-1940: Chinese troops have advanced 9.3 miles short of Gwangdzjow (Canton).
-
20-01-1940: British Secretary of the Navy Winston Churchill calls on neutral countries to join the Allies.
-
21-01-1940: The Finnish Department of War establishes a foreign legion of 11,500 volunteers from 26 countries.
-
23-01-1940: The peace declaration of the South-African opposition leader General Herzog is rejected with 81 against 59 votes.
-
25-01-1940: German aircraft bomb the British Shetlands.
-
25-01-1940: the Netherlands does not answer Churchill’s call to join the Allies.
-
26-01-1940: Soviet forces breach the Mannerheim line in Finland.
-
27-01-1940: The O.K.W. starts preparations for the occupation of Norway and Denmark, Unternehmen Weserübung.
-
29-01-1940: German aircraft bomb the British east coast from the Shetlands to Kent.
-
30-01-1940: In Tokyo, the Soviet-Japanese talks about the determination of the border between Outer-Mongolia and Manchuria are aborted.
-
30-01-1940: Hitler orders to draft a new plan of attack, This time for the whole of the Netherlands.
-
31-01-1940: The Dutch government urges General Reijnders to apply for his discharge.
-
01-02-1940: Kyosti Kollio (chairman of the Finnish parliament) states his country is ready to sign a peace treaty with the Soviet Union.
-
01-02-1940: Soviet forces launch an offensive on the Karelian isthmus.
-
02-02-1940: Japanese troops occupy Pinjang the Chinese province of Gwangxi.
-
03-02-1940: The Luftwaffe bombs the English coast between Tyne and Norfolk, sinking 14 vessels.
-
04-02-1940: Japanese bombing attacks cause much damage to the railway traffic between Haiphong and Kunming in China.
-
04-02-1940: The Balkan-Entente wishes to remain neutral.
-
05-02-1940: The Allied supreme command decides to dispatch three or four divisions to Norway in order to support the Finns and occupy the Swedish ore mines around Gällivare.
-
06-02-1940: The Dutch government announces its intention to construct three battle cruisers and to modernize the naval base at Surabaya on the island of Java, Indonesia.
-
06-02-1940: The Dutch Commander-in-Chief Reijnders receives an honorable discharge and is succeeded by General H.G. Winkelman.
-
08-02-1940: Soviet forces report the capture of various fortresses on the Mannerheim line in Finland.
-
12-02-1940: Germany and the Soviet Union sign an economic treaty.
-
12-02-1940: The first deportation of Jews from Szczecin to Lublin in Poland.
-
12-02-1940: The first Australian forces arrive in Suez, Egypt.
-
14-02-1940: The British merchant fleet in the North Sea is provided with weapons.
-
15-02-1940: The Kriegsmarine announces she will consider British merchant men as war ships.
-
15-02-1940: The British government offers to provide convoy protection to all neutral shipping, regardless of destination.
-
16-02-1940: The German supply vessel Altmark is boarded by the British destroyer H.M.S. Cossack in the Jösenfjord in Norway. 300 British PoWs are liberated.
-
17-02-1940: China reports a devastating defeat of Japanese forces near Nanning.
-
17-02-1940: The Swedish government refuses military aid to Finland.
-
18-02-1940: Chinese authorities report Japanese forces have landed on the Leidzjov isthmus in China.
-
23-02-1940: Allies declare a blockade in the Northern Arctic Sea to prevent Germany from importing high grade ore.
-
24-02-1940: The definite plan for Fall Gelb is completed.
-
25-02-1940: During a conference in Copenhagen, Denmark, the Scandinavian countries declare themselves neutral in the Finnish-Soviet conflict.
-
26-02-1940: The American Neutrality Board imposes strict restrictions on ships of belligerent nations in American home waters.
-
27-02-1940: Moscow reports the first Soviet victory at the front in northern Finland near Petsjenga since Christmas.
-
28-02-1940: The Soviet Union grants Finland 48 hours to accept the peace proposals.
-
28-02-1940: Soviet forces stand at 6.2 miles from Viipuri in Finland.
-
29-02-1940: The French government revalues its gold stock to be able to meet the war expenditures.
-
01-03-1940: British aircraft drop pamphlets over Berlin and other cities.
-
01-03-1940: Soviet forces reach the suburbs of Viipuri, Finland
-
02-03-1940: The New Zealand government announces to bring her fleet up to war footing and to reinforce the British navy with men.
-
03-03-1940: Soviet forces cross the frozen Bay of Viipuri, sealing the fate of the city.
-
03-03-1940: Norway and Sweden refuse an Allied expeditionary force passage to Finland.
-
04-03-1940: Romania rejects Italy’s offer to join the Anti-Kominternpact.
-
06-03-1940: The Dutch submarine O 11 collides with the Hr. MS BV 3 in the port of Den Helder. Three crew members are killed.
-
07-03-1940: Finnish supreme commander Carl Mannerheim considers continuing the battle useless and wants negotiations with the Soviets.
-
07-03-1940 - 07-03-1940: In the night of March 7th – 8th, the German steamer Hannover is intercepted and boarded by British H.M.S. Dunedin and Canadian H.M.C.S. Assiniboine. The vessel is transferred to Jamaica, to be rebuilt later in England as H.M.S. Audacity.
-
08-03-1940: A Finnish delegation, led by Prime Minister Risto Ryti leaves for Moscow to enter into negotiations with the Soviet Union.
-
12-03-1940: The Finnish-Soviet peace treaty is signed in Moscow. Finland is forced to cede the Karelian isthmus and the west bank of Lake Ladoga.
-
14-03-1940: The evacuation of inhabitants of the territory ceded to the Soviet Union gets under way.
-
15-03-1940: During a secret meeting, the French senate sharply criticizes France’s war policy.
-
16-03-1940: The Germans bomb the naval base at Scapa Flow in Scotland.
-
17-03-1940: Architect Fritz Todt is appointed Reichsminister für Rüstung und Munitionen.
-
18-03-1940: Hitler, Mussolini and Count Ciano meet on the Brenner. Mussolini declares he is willing to denounce the treaty of friendship with Great Britain and France.
-
19-03-1940 - 19-03-1940: Fifty RAF aircraft bomb the airbase at Hörnum on the German North Sea island of Sylt. This is the first RAF attack on a target on German territory.
-
20-03-1940: The cabinet of French Premier Daladier is dissolved as a result of the criticism on the war policy. Paul Reynaud is appointed the new premier.
-
20-03-1940: A British convoy is attacked off the Scottish coast by German aircraft. Nine vessels are sunk.
-
21-03-1940: French Premier Paul Reynaud forms a five-man War Cabinet.
-
23-03-1940: General Winkelman has new memoranda drafted on his war policy in order to submit them to the Dutch delegations in Brussels, Paris and London.
-
24-03-1940: On occasion of the Easter holiday, the Luftwaffe drops flowers over the French positions at the front.
-
24-03-1940: In his Easter address, the Pope condemns the belligerent nations for violating their treaties and their lack of humanity.
-
25-03-1940: The British government announces all legal means will be applied to prevent Germany from importing iron ore from the Norwegian port of Narvik.
-
28-03-1940: The Allied supreme command decides to lay mines in Norwegian home waters and to occupy some important positions.
-
28-03-1940: British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and French Premier Paul Reynaud declare not to sign a peace treaty or an armistice with Germany separately.
-
02-04-1940: The chairman of the Egyptian Wafda party demands of all British soldiers to leave the country as soon as the war is over and that all disagreements with Caïro be settled.
-
02-04-1940: Hitler sets the date for Unternehmen Weserübung (invasion of Denmark and Norway) at April 9th.
-
03-04-1940: Air Marshal Charles Portal is appointed Commander-in-Chief of R.A.F. Bomber Command, succeeding Air Chief Marshal Sir Edgar Ludlow-Hewitt who becomes inspector-general of the R.A.F.
-
04-04-1940: The Supreme Soviet approves a record budget for the defense and annexes the Karelian isthmus.
-
04-04-1940: The Dutch military attaché in Berlin informs the Norwegian envoy about German plans for an attack on Denmark and Norway. The envoy fears a British attack more.
-
05-04-1940: The Allied plan to lay mines in Norwegian home waters is postponed until April 8th.
-
05-04-1940: Speech of British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain at a meeting of the Conservative Party: "Hitler has missed the bus."
-
07-04-1940: Finland and the Soviet Union enter political relations again.
-
07-04-1940: Embarkation of a British expeditionary force for Norway. British mine layers set sail. German naval units set course for Denmark and Norway.
-
08-04-1940: The U.S.A. declares she will protect Dutch East Indies in case the Netherlands becomes involved in the war.
-
08-04-1940: British vessels lay mines in Norwegian home waters, the Norwegians protest.
-
08-04-1940: The Polish submarine ORP Orzel sinks the German freighter SS Rio de Janeiro. 180 German soldiers are killed. 150 people are rescued.
-
08-04-1940: The British destroyer HMS Glowworm is sunk by the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper. Of the 149 on board, 109 are killed.
-
09-04-1940: German troops invade Denmark and Norway (Unternehmen Weserübung) and occupy Copenhagen.
-
09-04-1940: King Haakon and his government leave Oslo and move to Hamar.
-
09-04-1940: Norwegian Vidkun Quisling announces in a radio speech he has formed a new national government with himself as Premier.
-
09-04-1940: German forces come ashore in Norway near Larvik, Oslo, Kristiansand, Stavanger, Bergen, Trondheim and Narvik.
-
10-04-1940: The Allies warn the (Belgian?) government of an imminent German invasion. The Belgian government declares to maintain her neutrality.
-
11-04-1940: The B.B.C. starts transmitting a program in Dutch.
-
12-04-1940: Japan promises to reopen the river Dzjoedzjiang (Pearl) in China - which has been closed since 1938 - for trade on April 20th.
-
12-04-1940: The Allies declare the Danish merchant navy to be owned by the enemy and begin holding Danish vessels in foreign harbors.
-
14-04-1940: Japan declares she will apply violence in case Dutch East Indies is occupied by a third party.
-
14-04-1940: British and French troops land in the Norwegian cities of Narvik, Namsos and Andalsnes.
-
14-04-1940: Five German destroyers and a U-boat are sunk off the Norwegian coast. Politics
-
15-04-1940: An Allied attempt at landing near Narvik is repulsed by the Germans.
-
15-04-1940: Norwegian Vidkun Quisling resigns as Prime Minister and is succeeded by Ingolf Christensen.
-
16-04-1940: British troops occupy the Fär-Oër islands and land near Namsos in Norway.
-
17-04-1940: The Luftwaffe bombs the British naval base Scapa Flow from the recently captured bases in Norway.
-
17-04-1940: The U.S. demands of Japan to leave the Dutch East Indies alone.
-
18-04-1940: The Japanese army reports having defeated Chinese troops in the northeastern province of Sjanxi.
-
18-04-1940: Danish army and navy personnel is sent home on leave; for them the war is over.
-
18-04-1940: German troops capture the fortresses of Oskarborg and Dobrak in the Oslo fjord, Norway.
-
18-04-1940: British troops land near Andalsnes, Norway.
-
19-04-1940: The Dutch Minister President De Geer announces in a speech on radio a state of siege has been proclaimed.
-
20-04-1940: British aircraft bomb Stavanger and Kristiansand in Norway to prevent German aircraft from landing.
-
20-04-1940: French troops land in Norway.
-
20-04-1940: Arnold Meijer changes the name Zwart Front (black front) to Nationaal front.
-
21-04-1940: Heavy fighting near Namsos, Trondheim and Narvik in Norway.
-
22-04-1940: German aircraft bomb the Norwegian city of Dombas.
-
22-04-1940: Sweden protests again violation of her air space by German aircraft.
-
23-04-1940: Egyptian Premier Ali Maher Pasja confirms his country has sided with the Allies.
-
23-04-1940: The Norwegian city of Gratangen – 25 miles north of Narvik – is taken from the Germans by British and Canadian troops.
-
24-04-1940: Berlin hushes the Swedish protest about aircraft flying over but does not promise to stop it.
-
24-04-1940: Adolf Hitler appoints Gauleiter Joseph Terboven Reichskommissar für die besetzte Gebiete in Norwegen (occupied areas in Norway).
-
26-04-1940: Belgian Premier Hubert Pierlot submits the resignation of his government to the King; it is rejected however due to the tense international situation.
-
26-04-1940: German troops breach the Allied front near the Norwegian town of Roros.
-
27-04-1940: The Allied supreme command decides to evacuate its troops from Norway.
-
28-04-1940: Rudolph Höss is appointed commander of camp Auschwitz.
-
28-04-1940: The Norwegian city of Namsos is heavily bombed by the Germans.
-
28-04-1940: The Allies abandon the plan to capture the Norwegian city of Trondheim.
-
28-04-1940: Marvin Breckinridge of Columbia Broadcasting System interviews Mussert; the so-called crossed arms talk.
-
30-04-1940: German troops advancing northwards from Oslo and southwards from Trondheim meet near Dombas.
-
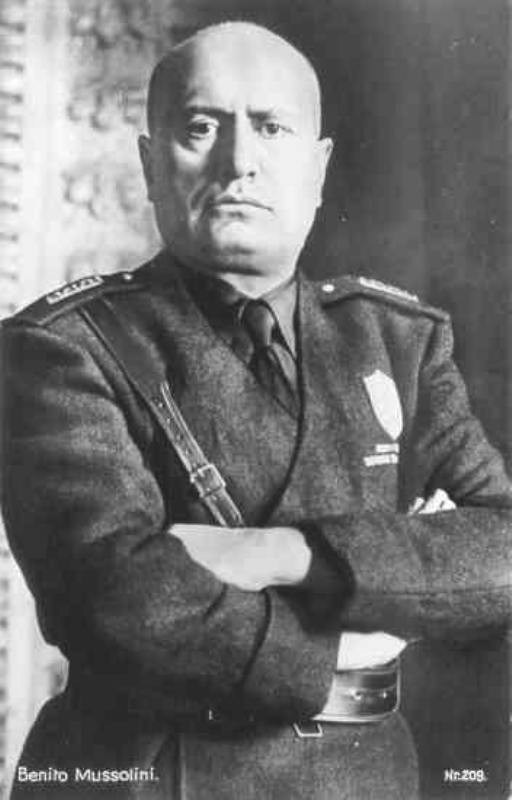
01-05-1940: American President Roosevelt sends Mussolini a message, warning him against Italy’s participation in the war on German side.
-
01-05-1940: Norwegian forces capitulate near Lillehammer.
-
01-05-1940: The Dutch Shipping Committee is established in New York.
-
02-05-1940: The Allies abandon their ports of debarkation in southern and central Norway.
-
02-05-1940: King Haakon of Norway and his family flee to Great Britain through the port of Moplde.
-
02-05-1940: German troops close in on Andalsnes. The Allies evacuate their troops in Namsos.
-
03-05-1940: 21 members of the N.S.B., fascists and Communists are arrested in the Netherlands. they are interned in camp Ooltgensplaat on the island of Walcheren.
-
03-05-1940: The Allies abandon the front line near the Norwegian city of Steinkjer and apply to the German supreme command for an armistice.
-
05-05-1940: German aircraft sink three destroyers escorting the convoy transporting the evacuated men.
-
05-05-1940: A Norwegian government in exile, headed by Premier Johan Nygaardsvold, is formed in London
-
08-05-1940: Japanese forces breach the Chinese defensive line between Hubei and Henan.
-
09-05-1940: The Belgian military attaché in Berlin warns his government for an imminent German invasion.
-
09-05-1940: The Dutch military attaché in Berlin, Major G.J. Sas warns his government for an imminent German invasion.
-
09-05-1940: British troops land on Iceland in order to protect the island.
-
09-05-1940: Hitler grants amnesty to Norwegian prisoners of war.
-
09-05-1940: At 20:45 in the evening, general headquarters issues a warning telegram that is not received by all, among others by the men at the Moerdijk bridges.
-
10-05-1940: In the early morning hours, German troops advance into the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxemburg and France.
-
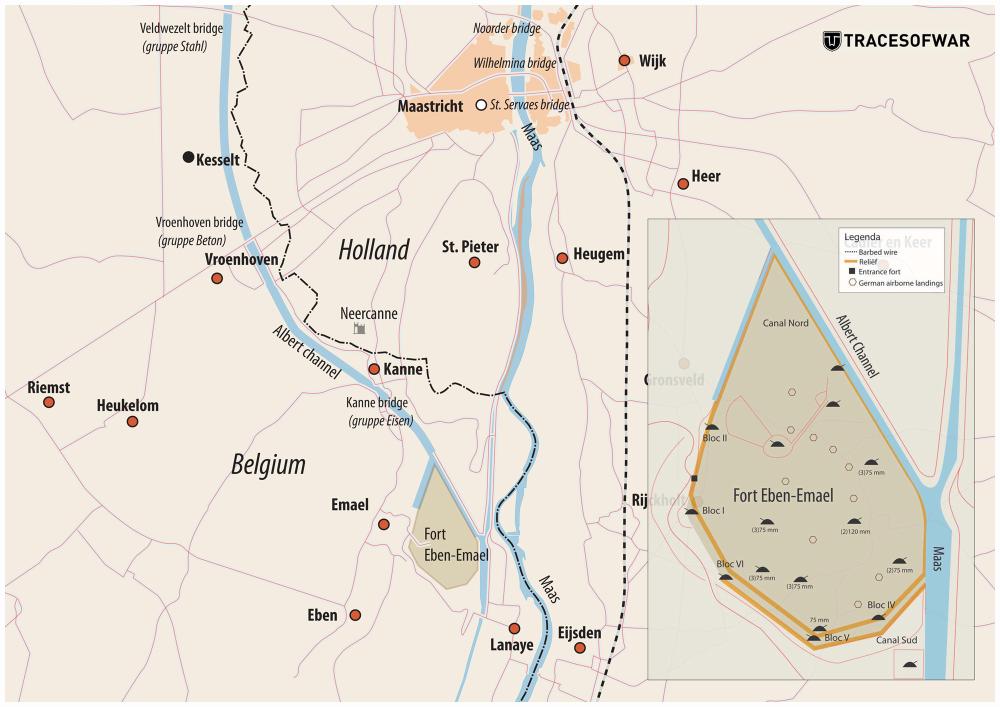
10-05-1940: German para troops land near bridges in Rotterdam, Dordrecht, the Moerdijk and on the roof of Belgian Fortress Eben-Emael. They also land near Dutch air fields.
-
10-05-1940: French and British troops cross the Franco-Belgian border.
-
10-05-1940: Heavy fighting is reported on the Ijssel and Grebbe lines. The positions on the river Meuse and the Peel are attacked.
-
10-05-1940: The Luftwaffe bombs cities such as Brussels, Antwerp, Calais, Dunkirk and Boulogne. Netherlands and Belgium
-
10-05-1940: Belgian King Leopold condemns the German invasion. Parliament passes a law allowing public servants to represent the government.
-
10-05-1940: British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain steps down and is succeeded by Winston Churchill.
-
10-05-1940: Queen Wilhelmina condemns the German invasion, Secretary van Kleffens travels to London in order to ask for help.
-
10-05-1940: The Dutch government interns Germans and members of the N.S.B. and proclaims the state of siege in Dutch East Indies.
-
10-05-1940: The Dutch destroyer Hr. Ms. Van Galen, steaming to Rotterdam, is sunk in the Nieuwe Waterweg by German air raids. One person is killed.
-
11-05-1940: Churchill forms a war cabinet and gives the R.A.F. permission to bomb targets in Germany.
-
11-05-1940: German forces encircle Liege. The fortress Eben-Emael surrenders and various Belgian cities are bombed.
-
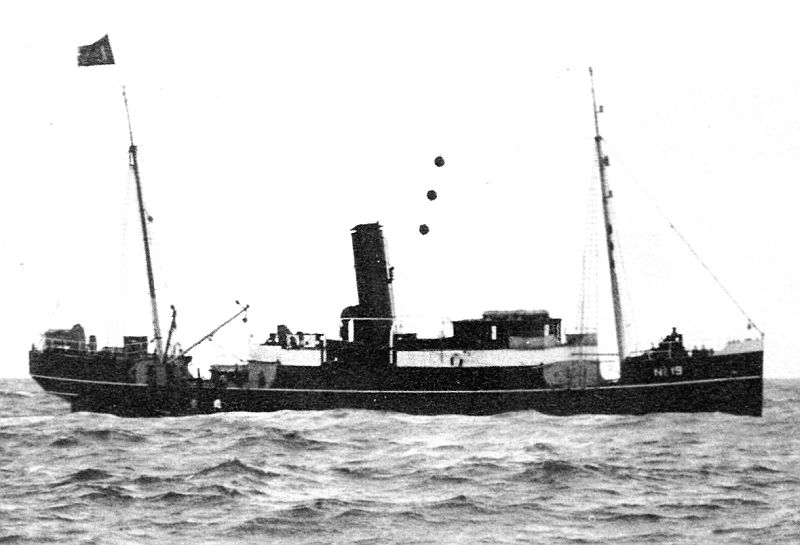
11-05-1940: The Dutch steam pilot vessel Hr. Ms. BV 19A, with 22 million guilders in gold bars on board, runs on a magnetic mine in the Nieuwe Waterweg and sinks. Thirteen crew members and three British soldiers are killed.
-
12-05-1940: Princess Juliana, Prince Bernhard and their two daughters leave for England.
-
12-05-1940: The city of Breda, the northernmost tip of the French defensive line, is evacuated; some 50,000 civilians leave the city and head for Antwerp.
-
12-05-1940: German troops occupy the French city of Sedan, cross the Albert canal near Liege and reach the river Meuse at Dinant.
-
12-05-1940: Meeting at Cateau between King Leopold, Daladier and representatives of the Belgian, French and British General Staff. King Leopold is placed under Allied command.
-
12-05-1940: The Dutch gunboat Hr. Ms. Friso is sunk in the IJsselmeer. Three people are killed.
-
13-05-1940: Churchill presents his new government and promises the British population hard work, blood, sweat and tears.
-
13-05-1940: On advice by the government, Queen Wilhelmina leaves for London, followed by the government later in the day.
-
13-05-1940: British forces land near Narvik in Norway.
-
13-05-1940: The German army captures Liege and Dinant and has crossed the river Meuse in various places. Politics
-
13-05-1940 - 13-05-1940: The British Harpoon Force lands at Hook of Holland. This force, consisting of 651 men, aims to advance to The Hague and bring the Dutch government to safety. They are evacuated the next day. As a result of German air raids, they regret 11 deaths.
-
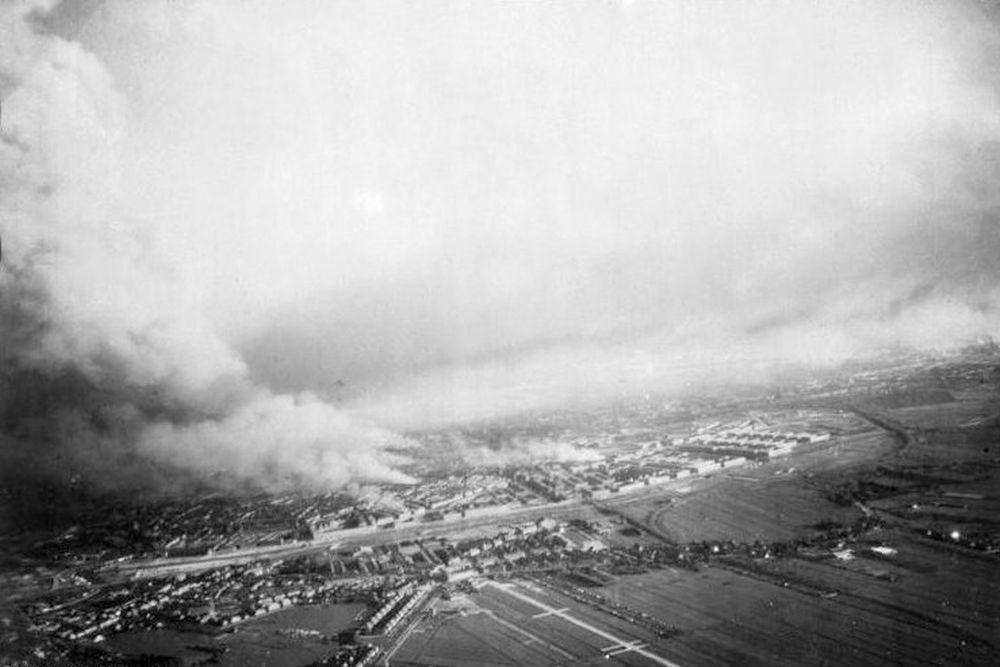
14-05-1940: The city of Rotterdam is subjected to a heavy bombardment.
-
14-05-1940: Negotiations between Premier Pierlot and King Leopold. The King refuses to pull the Belgian forces back to France.
-
15-05-1940: The capitulation of the Dutch army is signed at 11:00 hours in Rijsoord, the Netherlands.
-
15-05-1940: German armored forces achieve a break through near Sedan.
-
15-05-1940: The Dutch gunboat Hr. Ms. Johan Maurits van Nassau is sunk by German bombers ten miles west of Callantsoog, while on her way to Great Britain. 17 crew members are killed.
-
15-05-1940 - 15-05-1940: Engagements of Dutch, French and Belgian forces in Zeeland.
-
16-05-1940: The Belgian government moves her seat to Ostend.
-
16-05-1940: The French government announces she will not leave Paris.
-
16-05-1940: The British Expeditionary Force withdraws to the west of Brussels.
-
16-05-1940: The French 9th army is routed between the rivers Sambre and Meuse; General Giraud is taken prisoner near La Capelle.
-
16-05-1940: The first press conference in the Netherlands to take place under supervision by the Presseabteilung der Hauptabteilung Volksaufklärung und Propaganda (press department of the main department of popular education and propaganda). This marks the beginning of the equalization of the Dutch press.
-
16-05-1940: The first large-scale attack by the British Air Force on the Ruhr area takes place. The damage inflicted is minimal, but later this is seen as the beginning of the strategic bombing campaign.
-
17-05-1940: Hitler orders tank commander Guderian to halt his fast advance and so enable the infantry to catch up.
-
17-05-1940: Order of the day by French General Gamelin: "The fate of our home country is at stake".
-
17-05-1940: The Belgian army abandons the line Antwerp-Louvain. German troops march into Brussels.
-
17-05-1940: A German bombing raid on the girls' school Institute Onze-Lieve-Vrouw-Immaculate in Sint-Niklaas killed 54 people, 51 of them evacuees from Breda.
-
18-05-1940: German troops occupy the city of Antwerp.
-
18-05-1940: The Belgian government decides to leave the country; King Leopold decides to stay behind with four ministers including Pierlot, Spaak and Denis.
-
18-05-1940: Brussels is ceded to the Germans at 18:00 hours.
-
18-05-1940: In France, Maréchal Pétain is appointed vice-Premier.
-
18-05-1940: St. Quentin and Cambrai are in German hands.
-
18-05-1940: German troops cross the river Sambre and reach Amiens.
-
18-05-1940: The resistance group De Geuzen spread their second Geuzen message.
-
19-05-1940: Arthur Seyss-Inquart is appointed Reichsminister für die besetzte Niederlände (minister for occupied Holland).
-
19-05-1940: Meeting between Lord Gort, Commander of the B.E.F. and General Billote. These negotiations make the British War Office consider the withdrawal of the B.E.F. to Great Britain.
-
19-05-1940: General Gamelin is replaced as supreme commander of the French armed forces by General Weygand.
-
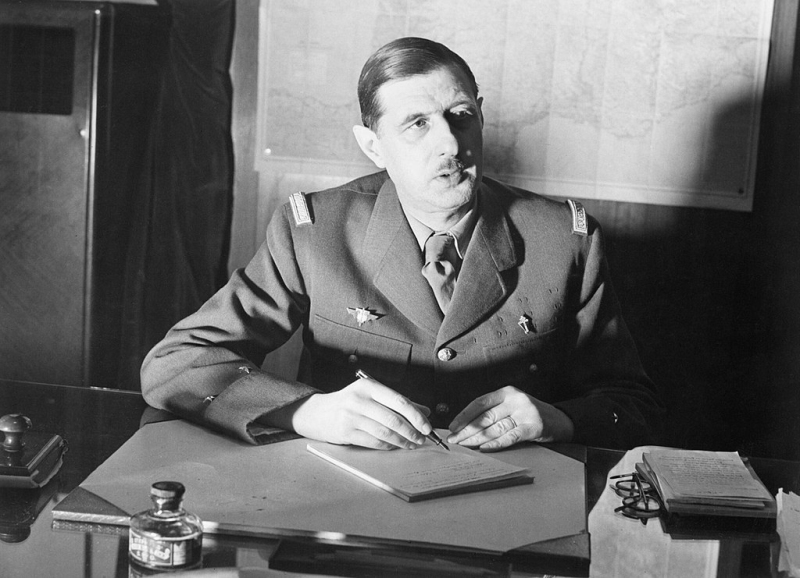
19-05-1940: An armored attack across the river Serre, led by General de Gaulle against troops of Guderian fails.
-
20-05-1940: Belgian Verdinaso leader Joris van Severen is murdered in Abbéville by French soldiers, along with 21 other political prisoners.
-
20-05-1940: Thirty German criminals arrive from Sachsenhausen at Auschwitz Concentration Camp to prepare for use as a prison camp for Polish prisoners.
-
20-05-1940: German forces capture the towns of Atrecht, Laon and Amiens, units of scouts reach Abbéville.
-
20-05-1940: The Belgian army retreats beyond the Scheld and the canal Gent – Terneuzen.
-
21-05-1940: German troops are some 62 miles from Paris and have nearly reached the French coast. The evacuation of Parisians gets under way.
-
21-05-1940: King Leopold, Lord Gort and General Weygand have a meeting in Ypre to discuss the situation.
-
21-05-1940: An Allied offensive southward from Arras fails. The town is taken by the Germans.
-
22-05-1940: The German ambassador in Tokyo informs the Japanese Secretary of Foreign Affairs Germany is not interested in Dutch East Indies.
-
22-05-1940: German armored divisions commanded by Heinz Guderian reach the outskirts of Boulogne and Calais.
-
22-05-1940: A French counter offensive near Kamerrijk fails.
-
22-05-1940: Churchill pays a visit to General Weygand in Vincennes. The Belgian army will retreat across the river Ijzer.
-
23-05-1940: Belgian forces abandon the city of Gent.
-
23-05-1940: The ports of Dunkirk and Dover are bombed by German aircraft.
-
23-05-1940: British troops abandon the French city of Atrecht.
-
23-05-1940: Lord Gort, commander of the B.E.F. urges evacuation. The British troops withdraw from the front at Arras.
-
24-05-1940: An announcement is made in Paris to the effect that all Belgian art treasures have been smuggled out of the country during the German invasion.
-
24-05-1940: The head of the Dutch Department of Social Affairs, Arend Scholtens, informs all city councils that an unemployed worker, who refuses to work in Germany, shall no longer receive social security.
-
24-05-1940: German troops capture the port of Calais.
-
24-05-1940: The Belgian army retreats behind the Leie and its tributary.
-
24-05-1940: King Leopold announces he will share the fate of the Belgian soldiers, whatever happens.
-
24-05-1940: Hitler orders General Guderian, who is on the point of entering Dunkirk, to halt his advance. The fighting in that area is to be left to the Luftwaffe.
-
24-05-1940: King Leopold has a meeting with Secretaries Pierlot, Spaak and Denis about the untenable military situation.
-
25-05-1940: German troops capture Boulogne-sur-Mer.
-
26-05-1940: Belgian Prime Minister Hubert Pierlot and two Secretaries leave for Paris via Great Britain.
-
26-05-1940: British General Lord Gort is ordered to withdraw the B.E.F. to the Channel coast; Operation Dynamo, the evacuation from Dunkirk has begun. Hitler orders Guderian to resume his armored attack on Dunkirk.
-
26-05-1940: Calais falls in German hands.
-
27-05-1940: Dutch General Winkelman prohibits Secretary-general of Defense, C. Ringeling and the manager of Hoogovens to make military efforts for Germany.
-
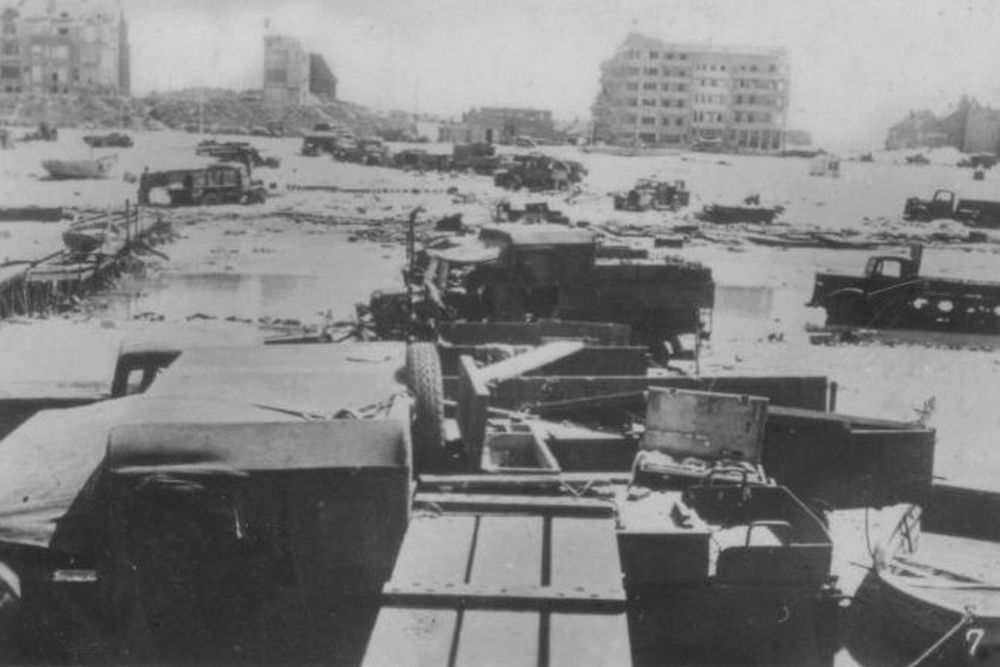
27-05-1940: On the beaches at Dunkirk, some 338,000 Allied soldiers assemble to be evacuated. The Luftwaffe bombs Dunkirk to rubble and fires at the evacuation vessels.
-
27-05-1940 - 27-05-1940: Operation Dynamo: evacuation of the B.E.F. from Dunkirk.
-
28-05-1940: King Leopold III signs the capitulation of the Belgian army.
-
28-05-1940: The Belgian Pierlot government, assembled in Poitiers, France, indicates her willingness to continue the fighting and takes executive power away from King Leopold III.
-
28-05-1940: British, French, Norwegian and Polish troops drive the Germans out of Narvik, Norway
-
28-05-1940: Some 850 vessels assemble off the British coast in order to evacuate the surrounded army at Dunkirk.
-
29-05-1940: German troops occupy the French coast, except for a narrow stretch near Dunkirk.
-
29-05-1940: Dr. Arthur Seyss-Inquart, Reichskommissar für die besetzten Niederländische Gebiete, delivers his inaugural address in the Ridderzaal in the Hague: "Protecting the rights of the Dutch population".
-
30-05-1940: Mussolini informs Hitler Italy will join in the war.
-
31-05-1940: General Alexander von Falkenhausen is appointed commander of the German armed forces in Belgium, northern France and Luxemburg.
-
31-05-1940: Belgian members of parliament in Limoges, who have fled, declare the signing of the capitulation by King Leopold to be unconstitutional.
-
31-05-1940: President Roosevelt announces the Million dollar Defense program.
-
01-06-1940: The city of Lille surrenders.
-
01-06-1940: In a notice to the Germans, Staf de Clerq, leader of the VNV (Flemish National Union) declares himself willing to cooperate.
-
01-06-1940: In the Netherlands, Jews are banned from holding posts in air defenses.
-
01-06-1940: Hitler arrives in Brussels for a visit to Belgium and France. At Brussels Evère airport, he is welcomed by Von Bock, Von Brauchitsch, Kesselring, Von Küchler and Von Reichenau.
-
01-06-1940 - 01-06-1940: The Germans draft plans to deport all Jews to the island of Madagascar.
-
03-06-1940: Paris is bombed by the Germans.
-
04-06-1940: Churchill delivers a speech entitled: "We shall fight on the beaches".
-
04-06-1940: Operation Dynamo is completed. 338,226 men are evacuated from Dunkirk including some 100,000 men from other countries, mainly France. The Germans lose 150 aircraft, the British 106. Major-general Harold Alexander is the last soldier to leave Dunkirk.
-
04-06-1940: In The Hague, representatives of Dutch metal works negotiate with Freiherr von Schrotter, Rüstungsinspektor der Deutschen Wehrmacht (inspector of equipment of the German Wehrmacht) about cooperation with the German occupier.
-
04-06-1940: Neuengamme concentration camp becomes an independent camp.
-
04-06-1940 - 04-06-1940: Evacuation of Allied troops from Norway.
-
05-06-1940: Start of Fall Rot (Case Red), the second German offensive in France.
-
05-06-1940: Ir. A.A. Mussert pays his first visit to Seyss-Inquart. He urges Mussert to reinforce the N.S.B. (National Socialist Movement) and help win the Dutch population over to National Socialism.
-
06-06-1940: General Rommel breaches the Somme front near Amiens.
-
06-06-1940: The Netherlands: Coffee and tea are on ration.
-
06-06-1940: The Secretary of Defense in London is authorized by Royal Decree to set up measures, enabling Dutchmen, not liable for military service and other Dutch citizens to render mandatory personal service to or for shipping.
-
07-06-1940: Göring, Beauftragte für den Vierjahresplan (Director of the Four Year Plan) declares that in the economic field, the Netherlands will be treated no better or worse than Germany.
-
08-06-1940: Evacuation of Allied troops from Narvik.
-
08-06-1940: King Haakon of Norway and his government flee to England from Tromsö.
-
08-06-1940: The German battleships Scharnhorst and Gneisenau sink three British merchantmen as well as the aircraft carrier H.M.S. Glorious and three British destroyers.
-
09-06-1940: The Germans occupy Rouan.
-
09-06-1940: The Germans launch the offensive on the Aisne front.
-
09-06-1940: Norway capitulates.
-
10-06-1940: Italy declares war on Great Britain and France. Canada declares war on Italy.
-
11-06-1940: The French government leaves Paris and takes up residence in Tours.
-
11-06-1940: German troops reach Reims.
-
11-06-1940: Churchill meets Reynaud in Briare and asks him to continue fighting.
-
11-06-1940: Australia, New Zealand and South-Africa declare war on Italy.
-
11-06-1940: The British Admirality announces that the Polish submarine ORP Orzel has perished, killing all 63 crew members.
-
12-06-1940: Spain declares herself non-belligerent.
-
12-06-1940: British aircraft bomb the Italian base at Tobruk, Libya.
-
12-06-1940: The Dutch submarine Hr. Ms. O 13 departs on a war patrol for the Skagerrak. After that, nothing more is heard from the ship. The submarine probably ran into a German mine, killing all 34 crew members.
-
13-06-1940: Paris is declared an open city. The French government decides to move to Bordeaux.
-
13-06-1940: Negotiations between Churchill and Reynaud.
-
13-06-1940: U.S. President Roosevelt signs a Navy Bill, making $ 1,3 billion available for improvements. On Churchill’s request, more weapons are sent across the Ocean.
-
14-06-1940: The Germans occupy Paris and Le Havre.
-
14-06-1940: The Soviet Union occupies Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Bessarabia and northern Bukovina.
-
14-06-1940: The French navy bombards the Italian ports of Gena and Vado.
-
15-06-1940: The French government has taken up residence in Bordeaux
-
15-06-1940: In Paris, the first Jewish committee for support is established, the Comité Amelot. This is an umbrella organization of various Jewish charity organizations.
-
15-06-1940: The Germans cross the Rhine and advance into France.
-
15-06-1940 - 15-06-1940: Evacuation of the remaining Allied troops from France. In Operation Gazelle, this action is expanded to include the Bay of Biscay.
-
16-06-1940: Reynaud steps down as France’s Prime Minister. A new government is formed with Maréchal Pétain as Prime Minister. The new government asks Germany via Spain about the conditions of an armistice.
-
17-06-1940: The Germans occupy the cities of Besançon, Metz, Dyon and Orléans.
-
17-06-1940: Maréchal Pétain delivers a speech on radio declaring the battle has to be ended. In the evening, Churchill also delivers a speech on radio stating that England will continue fighting on her own.
-
17-06-1940: In the Netherlands, bread and flour are rationed.
-
17-06-1940: The Germans cross the Loire.
-
17-06-1940: The British troop transport, the former passenger liner Lancastria is sunk by German aircraft in the port of St. Nazaire. Over 2,500 persons lose their lives.
-
18-06-1940: Churchill delivers a speech to the House Of Commons: "This was their finest hour".
-
18-06-1940: The leader of the Free French, General de Gaulle delivers a speech on radio urging to continue the fighting.
-
18-06-1940: Hitler and Mussolini meet in Munich.
-
19-06-1940: The German government announces she is willing to present the conditions for an armistice to France.
-
19-06-1940: Cherbourg falls in German hands.
-
20-06-1940: German troops occupy Strasbourg, Brest and Tours.
-
20-06-1940: U.S. President Roosevelt appoints two anti-isolationist Republicans in his cabinet; Henry Stimson as Secretary of War and Frank Knox as Secretary of the Navy.
-
22-06-1940: In Rethondes (Compiègne) France and Germany sign the armistice, effective as from June 25.
-
22-06-1940: The Italians launch their first offensive on the Alpine front.
-
22-06-1940: Landdag (meeting) of the N.S.B. in Lunteren. The N.S.B. expresses its loyalty to Hitler.
-
22-06-1940: The British detect the German guidance system Knickebein which operates with radio waves.
-
23-06-1940: Marcel Louette – a.k.a. Fidelio – establishes the resistance group de Witte Brigade (White Brigade) in Antwerp.
-
23-06-1940: Hitler visits Paris.
-
24-06-1940: Italian troops occupy Menton.
-
24-06-1940: France and Italy sign an armistice, effective as from 01:35 hours on June 25.
-
25-06-1940: The start of cooperation between the most prominent Protestant communions in the Netherlands.
-
26-06-1940: Romania agrees to the Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and northern Bukovina although Romanian forces attempt to stop the Red Army at the border.
-
28-06-1940: The British government acknowledges General de Gaulle as the leader of the Free French.
-
29-06-1940: Carnation day in the Netherlands. On occasion of the birthday of Prince Bernhard, demonstrations by Orange fans are held, in particular in The Hague.
-
30-06-1940: German forces occupy the Channel islands Guernsey and Jersey.
-
30-06-1940: The O.S.E., a Jewish organization for aid to children is relocated to Montpellier in France at the end of the year. From here, she starts actions in support of children and the sick; in particular in the summer of 1942, she will grew into an important resistance organization, the Garel circuit.
-
01-07-1940: The French government takes up residence in Vichy.
-
01-07-1940: The Politiek Convent (political convent) is established in the Netherlands.
-
01-07-1940: The Kertoso is the first Dutch vessel captured by the German raider Thor, disguised as a Yugoslav vessel named Vir.
-
01-07-1940: The German U-boats now have five ports on the west coast of France at their disposal and begin inflicting heavy losses on Allied convoys.
-
03-07-1940: Operation Catapult. British operation during which French naval units in the ports of Plymouth and Portsmouth are overpowered, French naval units in the port of Alexandria are confiscated and the French naval base Mers-el-Kébir is attacked.
-
04-07-1940: Seyss-Inquart issues an order, prohibiting the population to listen to a number of foreign radio stations in order to protect the population against incorrect information.
-
04-07-1940: The Vichy-French government severs all diplomatic ties with Great Britain.
-
05-07-1940: Sweden allows Germany to use her railway network for the transport of goods and unarmed troops.
-
08-07-1940: In the Dakar roads, the French battleship Richelieu is severely damaged by British aircraft.
-
09-07-1940: First engagement between British and Italian naval units off Punta Stilo in the Mediterranean.
-
09-07-1940: The R.A.F. starts nocturnal bombing of German cities.
-
09-07-1940: French warships in Alexandria harbor are neutralized.
-
10-07-1940: Start of the Battle of Britain.
-
11-07-1940: Vichy-France. By proclaiming a trio of constitutional measures, Maréchal Pétain draws all power to himself.
-
13-07-1940: Italian units attack the British garrison at Moyale in Egypt.
-
15-07-1940: Hitler decides to start preparations for an invasion of Great Britain.
-
15-07-1940: In the Netherlands rice, vermiculiet, corn flour, butter, margarine, fat and vegetable oil are rationed.
-
16-07-1940: H.J. Woudenberg of the N.S.B. is appointed manager of the N.V.V. (Dutch trade union).
-
16-07-1940: The Japanese army forces the pro-western government of Admiral Mitsumasa Yonay to resign.
-
17-07-1940: The German raider Thor sinks the Dutch merchantman Tela and takes the crew prisoner.
-
18-07-1940: In order to avoid a confrontation with Japan, the Burma road through which China receives its supplies, is closed by Great Britain for three months.
-
19-07-1940: Hitler makes his final bid for peace to Great Britain in a speech.
-
20-07-1940: Seyss-Inquart bans the Communistische Partij Nederland (Communist Party of the Netherlands).
-
21-07-1940: Hitler announces his intention to attack the Soviet Union in a speech on the Berghof.
-
21-07-1940: The Polish government in exile arrives in London from Paris.
-
21-07-1940: The Soviet Union officially annexes Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia.
-
22-07-1940: Lord Halifax rejects Hitler’s bid for peace of July 19.
-
22-07-1940: Japan: Prince Funimaru Konoye is appointed Prime Minister, Yosuke Matsuoka becomes Secretary of Foreign Affairs and General Tojo Secretary of Defense.
-
22-07-1940: In Great Britain, the Special Operations Executive or S.O.E. is established. Its purpose is secretly supporting resistance groups in occupied territory.
-
23-07-1940: Dr. Benes forms a provisional Czech government in exile.
-
24-07-1940: Mr. J. Linthorst Homan, prof. dr. E.J. de Quay and mr. Einthoven establish the Nederlandse Unie (Dutch Union).
-
25-07-1940: The Netherlands: footwear is rationed.
-
25-07-1940: The Netherlands: first newsletter by Pieter ‘t Hoen, an underground paper.
-
25-07-1940: The U.S.A. imposes restrictions on the export of oil and metals. This measure is targeted at Japan in particular.
-
28-07-1940: Radio Oranje transmits its first program from London.
-
30-07-1940: The French forces in North-Africa and Syria are demobilized.
-
31-07-1940: Great Britain imposes a blockade on France and her colonies
-
31-07-1940: The Netherlands: A ban on ritual slaughter is issued.
-
01-08-1940: Belgium: the intelligence network Zero is set up by Fernand Kerkhofs.
-
02-08-1940: In Gross Rosen, Silesia, a satellite camp of Sachsenhausen in erected.
-
03-08-1940: British Somaliland is attacked by Italy.
-
03-08-1940: "At their own request" Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania are incorporated into the Union of Socialist Soviet Republics.
-
07-08-1940: Great Britain approves the establishment of the army of the Free French of General de Gaulle.
-
17-08-1940: Hitler orders a blockade of the British isles.
-
19-08-1940: British troops withdraw from British Somalia. The country is now ruled entirely by the Italians.
-
20-08-1940: Churchill’s speech to the House of Commons: "Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few".
-
24-08-1940 - 24-08-1940: First German bombardment of London.
-
25-08-1940 - 25-08-1940: First British bombardment of Berlin in retaliation of the bombing of London.
-
26-08-1940: The Chad region sides with General de Gaulle.
-
27-08-1940: Mussert sends a memo to Hitler, requesting to integrate the Dutch population in a new Union of Germanic states.
-
27-08-1940 - 27-08-1940: Dropping of the Dutch CID agent Lodo van Hamel. He is one of the first intelligence agents to be parachuted over the Netherlands.
-
27-08-1940 - 27-08-1940: Romania cedes southern Dobrudsja to Bulgaria.
-
28-08-1940: French-Equatorial Africa and Cameroun side with General de Gaulle,
-
31-08-1940: The first edition of "Vrij Nederland" (The free Netherlands) is published.
-
31-08-1940: A three day conference is held by the so-called Lunteren Circle, a group of clergymen who had contacted the "Bekennende Kirche" (approving church) in Germany before the war.
-
01-09-1940: Hitler orders the Organisation Todt to construct heavily fortified U-boat pens in Brest, Lorient and St. Nazaire.
-
01-09-1940: An S.O.E. Section Norway is established in London.
-
01-09-1940: The first Norwegian S.O.E. agents begin training in Great Britain.
-
03-09-1940: In return for 50 W.W.1. destroyers from the U.S., England cedes bases on New Foundland, the West Indies and British Guyana.
-
03-09-1940 - 03-09-1940: Period of the first Gerbrandy cabinet.
-
04-09-1940: In a speech, Hitler threatens to raze the English cities to the ground (ausradieren).
-
05-09-1940: Vichy-France severs diplomatic ties with Belgium, Luxemburg, the Netherlands and Norway.
-
05-09-1940 - 05-09-1940: Period of heavy attacks by the Luftwaffe on London by day and night. It is also the beginning of the aerial attacks on British economic potential.
-
06-09-1940: King Carol of Romania abdicates in favor of Prince Michael.
-
07-09-1940: The first heavy air raids by the Luftwaffe on London by day.
-
11-09-1940: Hitler postpones the landings in England for three days and again on September 14 and 17.
-
13-09-1940: Italian troops attack Egypt. Sollum is occupied.
-
15-09-1940: ‘Battle of Britain Day’: 56 German and 26 British aircraft are lost.
-
16-09-1940: The Dutch branch of the SS is established.
-
16-09-1940: In the Netherlands, meat and meat products are rationed.
-
18-09-1940: Italian troops take Sidi Barani.
-
19-09-1940: Vichy-France puts troop ashore near Dakar. This is a defensive measure against a possible landing by Free French commanded by General de Gaulle.
-
20-09-1940: Polizeihaftlager (prison camp) Breendonck near Antwerp is put into use.
-
20-09-1940: New-Caledonia sides with General de Gaulle.
-
23-09-1940: The raid by the Free French on Dakar fails.
-
23-09-1940: Vichy-France severs diplomatic ties with the Polish government in exile.
-
23-09-1940: Ir. A.A. Mussert visits Hitler in Berlin for the first time.
-
23-09-1940 - 23-09-1940: Berlin is bombed by 119 English aircraft.
-
27-09-1940: Germany, Italy and Japan sign the Tri-Partite-Pact.
-
28-09-1940: Deployment of German bombers on raids by day will be suspended gradually. First raids by fighter bombers on targets in London.
-
28-09-1940 - 28-09-1940: Period of air raids by Luftwaffe fighter bombers on London, mostly during daylight.
-
01-10-1940: Luciaan Meyer and Theo Simon establish the illegal Mouvement Nation Royaliste (N.M.R.) in Aerschot. Many officers are members of this organization. In the Netherlands, this movement is called the Nationale Koninklijke Beweging (N.K.B., National Royal Movement) but as an alias, the name of a gymnastic club is used: Naar Kultuur en Bekwaming (N.K.B., towards culture and skill).
-
01-10-1940: The Finnish government agrees to grant Germany a monopoly on the Finnish export of nickel in exchange for weapons.
-
01-10-1940: In Poland, the Germans launch Operation Otto, the improvement of road and railway links with the Soviet Union, deploying forced laborers.
-
01-10-1940: The Nationalist 89th Army attacks Chen Yi’s New Communist 4th Army near Taixing on the river Yangtse in China.
-
01-10-1940: The Japanese occupy Weihawei in China.
-
02-10-1940 - 02-10-1940: This night, 81 bombers of the R.A.F. attack targets in Germany, Eindhoven air field and the Channel ports.
-
03-10-1940: In Warsaw, all Jews are ordered to relocate to the ghetto.
-
03-10-1940: The British navy concludes a sweeping operation in the eastern Mediterranean, reinforcing the troops on Malta and sinking an Italian submarine by the destroyers H.M.S. Hasty and H.M.S. Havock.
-
03-10-1940: In England, Neville Chamberlain resigns for reasons of health. Kingsley Wood and Ernest Bevin join the War Cabinet.
-
03-10-1940: The Vichy-French government excludes Jews from all public and military functions without any pressure from Germany.
-
03-10-1940: Seven bombers of the R.A.F. fly sorties against Rotterdam, Dunkirk and Cherbourg by day.
-
04-10-1940: Hitler meets Mussolini on the Brenner pass.
-
04-10-1940: All Dutch civil servants are required to sign a declaration of Aryanism.
-
04-10-1940: England: Sir Charles Portal is appointed the new chief of the air staff; effective as from October 24. He replaces Sir Cyril Newall who is appointed governor of New Zealand. As successor to Portal as Commander-in-Chief Bomber Command, the name of Air Marshal Sir Richard Pierce is mentioned.
-
04-10-1940: Churchill asks Roosevelt to send ships as reinforcement of Singapore.
-
07-10-1940: German forces enter Romania pretending to train the troops of the Iron Guard. The real intention is the occupation of the oil fields near Ploesti.
-
07-10-1940: Vichy-France: Algerian Jews are stripped of their French citizenship.
-
08-10-1940: U.S.A.: the government advices U.S. nationals to leave the Far East.
-
09-10-1940: Winston Churchill succeeds Neville Chamberlain as leader of the Conservative Party.
-
09-10-1940: 108 bombers of the R.A.F. attack targets in Germany, including the battleship Tirpitz which lies in a dry dock in Wilhelmshafen.
-
09-10-1940: St. Paul’s cathedral in London is damaged by a bomb.
-
10-10-1940: A referendum in Luxemburg, organized by the Germans, shows that 97% of the population is against the occupation by the Nazis.
-
10-10-1940: The R.A.F. bombs German vessels in Cherbourg.
-
11-10-1940: Australia: According to the outcome of the general elections, Robert Menzies is granted a second term as Prime Minister.
-
11-10-1940: The British navy sinks three Italian naval vessels in the Mediterranean.
-
12-10-1940: Unternehmen Seelöwe (Operation Sea lion) is postponed to the spring of 1941.
-
14-10-1940: In Vichy-France, married women are excluded from government functions.
-
14-10-1940: In the Netherlands, an identification requirement will be introduced. From April 1941 official identity cards (persoonsbewijzen) will be issued.
-
15-10-1940: Hitler orders to dissolve the invasion fleet.
-
15-10-1940: The Italian War Council decides to capture Greece without informing Germany. The invasion is scheduled for the end of October.
-
15-10-1940: Secret agent Lodo van Hamel is arrested in Friesland (see August 27).
-
16-10-1940: The German administration orders the establishment of a ghetto in Warsaw.
-
16-10-1940 - 16-10-1940: The R.A.F. bombs Dunkirk and the harbors in Kiel. The British navy shells oil depots in Tromsö, Norway.
-
18-10-1940: The first truck loads of war supplies arrive in Kunming, China via the recently reopened Burma road. Great Britain refuses to accede to requests by Japan to close this road. Military supplies go to China, on the return trip, raw materials for export to the U.S.A.
-
18-10-1940: In Vichy-France, all Jews are now officially excluded from functions in the government, the industry, broadcasting companies and other influential functions.
-
19-10-1940: Four Italian bombers launch an attack on the British oil refinery in Bahrain. The British report no damage is inflicted.
-
19-10-1940: The Dutch East Indies agree to deliver 40% of her oil production over a period of 6 months, despite British efforts to prevent it.
-
20-10-1940: Attacks on London by German fighter bombers are suspended.
-
20-10-1940: The Netherlands: Cheese is rationed.
-
20-10-1940: Italian bombers attack Caïro for the first time.
-
20-10-1940: Germany: Count Helmuth James von Moltke writes a manifesto for his resistance group Kreisauer Kreis, named after his estate, containing a plan for a democratic post Nazi state.
-
22-10-1940: In the Netherlands, Winterhilfe (winter aid) is founded.
-
22-10-1940 - 22-10-1940: Deportation of 7,450 Jews from Baden, the Pfalz and the Saar region to camps in unoccupied France.
-
23-10-1940: Hitler meets Franco in Hendaye and tries to persuade him to join in the war.
-
24-10-1940: Hitler and Maréchal Pétain meet in Montoire.
-
24-10-1940: Joint protest by the Nederlands-Hervormde Kerk (Dutch Reformed Church), de Gereformeerde Kerken (Reformed Churches), de Remonstrantse Broederschap (Remonstrant Brotherhood) and the Algemeen Doopsgezinde Sociëteit (General Baptist Society) to Seyss-Inquart against the exclusion of Jewish civil servants.
-
25-10-1940: Belgian Premier Hubert Pierlot and Secretary of Foreign Affairs Paul Henri Spaak arrive in London. After their government had severed the diplomatic ties, they had traveled from Vichy-France to Spain where they were arrested. They managed to escape and traveled to London via Lisbon.
-
25-10-1940: R.A.F. bombers attack Berlin and Hamburg.
-
26-10-1940 - 26-10-1940: The R.A.F. bombs the Skoda armament factory in Pilzen, Czechoslovakia.
-
27-10-1940: General de Gaulle establishes the Conseil de Défense de l’Empire (Imperial Defense Council) in Brazzaville, Congo.
-
27-10-1940: Troops of the Free French commanded by General Larminat occupy Gabon in French-Equatorial Africa.
-
28-10-1940: Italian troops invade Albania from Greece; Hitler is furious.
-
28-10-1940: In Vichy-France, Pierre Laval is appointed Secretary of Foreign Affairs.
-
28-10-1940: Anthony Eden, General Archibald Wavell, General Jan Smuts and Emperor Haile Selassie meet in Khartoum to coordinate their objectives of the war.
-
28-10-1940: A state of war exists between Greece and Italy.
-
29-10-1940: The British navy attacks the Italian island of Stampalia.
-
30-10-1940: Radio address by Maréchal Pétain; he announces a policy of collaboration with Germany.
-
30-10-1940: Italian bombers attack Patras in Greece.
-
30-10-1940: An Italian attempt at sinking British vessels in Gibraltar using human torpedoes fails.
-
31-10-1940: British reinforcements arrive on Crete.
-
01-11-1940: In France, a secret intelligence service is established, Confrèrie Notre Dame led by Rémy.
-
02-11-1940: In the Netherlands, groats and groceries are rationed.
-
03-11-1940: End of a period of 57 nocturnal attacks on London carried out by 200 aircraft on average.
-
03-11-1940: British troops go ashore in Greece.
-
04-11-1940: In the Netherlands, eggs, gingerbread and cake are rationed.
-
05-11-1940: The Dutch submarine Hr. Ms. O 22 departs on a war patrol for the Norwegian coast. Subsequently nothing more is heard from the ship. The wreck was found on August 10, 1993. The submarine was probably sunk as a result of a technical defect, in which all 46 crew members were killed.
-
09-11-1940: England: Neville Chamberlain dies from abdominal cancer at the age of 71.
-
10-11-1940: Staf De Clercq, the leader of the Flemish National Union, announced in a speech that his party is open to cooperation with the German oppressor.
-
11-11-1940: The French colony Gabon sides with General de Gaulle.
-
11-11-1940: 21 British Swordfishes attack the Italian naval vessels in the port of Taranto. The battleship Conte di Cavour is sunk and two battleships, three cruisers and two destroyers are damaged. The Royal Navy gains the upper hand in the Mediterranean as a result of this air raid.
-
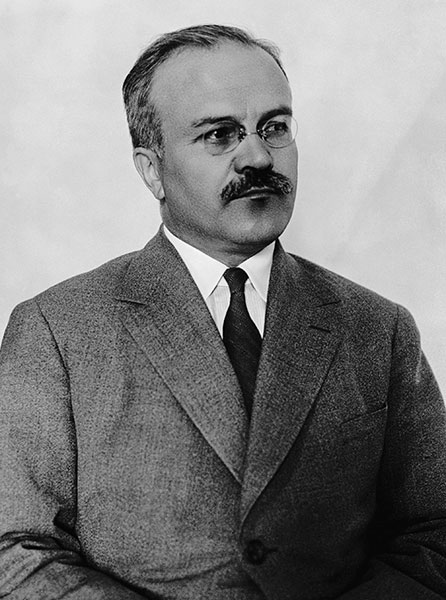
12-11-1940 - 12-11-1940: Soviet Secretary of Foreign Affairs, Molotov is in Berlin for talks with Hitler and Von Ribbentrop.
-
14-11-1940 - 14-11-1940: German air raid on Coventry: 500 tons of explosives and 30,000 incendiary bombs are dropped.
-
14-11-1940 - 14-11-1940: Period of nocturnal air raids by the Luftwaffe on cities in the country, on ports and on London.
-
19-11-1940: Italian troops have been pushed back beyond the river Kalamas.
-
20-11-1940: Hungary joins the Tri-Partite-Pact.
-
21-11-1940: The Belgian government in exile declares war on Italy.
-
23-11-1940: In the Netherlands, the first issue of the Communist paper De Waarheid (the truth) is published.
-
23-11-1940: Romania joins the Tri-Partite-Pact.
-
24-11-1940: Slovakia joins the Tri-Partite-Pact.
-
25-11-1940 - 25-11-1940: The Netherlands: students protest against the discharge of Jewish civil servants, professors and judges.
-
26-11-1940: Professor R.P. Cleveringa of Leiden State University delivers a speech on occasion of the discharge of his colleague, Jewish professor Eduard Meyers.
-
27-11-1940: The Netherlands: The universities in Leiden and Delft are closed down for an indefinite period.
-
28-11-1940: Der ewige Jude (the eternal Jew), a "documentary" about Jews has its premiëre in Berlin.
-
30-11-1940: In the Netherlands, the first issue of the Vrije Katheder (Free Lectern) is published.
-
01-12-1940: In Paris, the first issues of the underground resistance paper Libération Nord (liberation in the north), edited by Christian Pineau are distributed.
-
01-12-1940: The illegal Organisation civile et militaire (civil and military organization) is established in the northern zone of France.
-
01-12-1940: In December, judges of the Norwegian Supreme Court resign in protest against the Nazification of the judiciary system.
-
01-12-1940: Belgium: Secretary A. Delfoss and others establish the underground movement l’Armee de la Liberté (army of liberation). The focus of activities lies mainly in the region Liege.
-
01-12-1940: The Netherlands: Gas and electricity are rationed.
-
04-12-1940: Greek forces occupy Primeti and the Albanian port of Sarandia.
-
05-12-1940: Secret agreement between Great Britain and Vichy-France pertaining to the French colonial empire.
-
06-12-1940: Italy: supreme commander Marshal Pietro Badoglio is relieved of his function and is succeeded by General Count Cavallero.
-
07-12-1940: General Franco has a meeting with Admiral Canaris. Spain refuses to participate in the war. Consequently, Hitler is forced to abandon Unternehmen Felix, the occupation of Gibraltar.
-
09-12-1940: Start of Operation Compass, General Wavell’s counter offensive against the Italian forces in Cyrenaica.
-
10-12-1940: The British take Sidi Barani.
-
12-12-1940: Pact of eternal friendship between Yugoslavia and Hungary.
-
12-12-1940: Alfred Jodl, chief of the Wehrmachtführungsstab, receives a first draft plan of attack for an attack on the Soviet Union.
-
16-12-1940 - 16-12-1940: British air raid on Mannheim with 134 bombers. 34 people are killed and 240 buildings are destroyed.
-
17-12-1940: The British occupy Sollum.
-
17-12-1940: In Belgium, Aimé and Georges Dandoye establish the Mouvement National Belge (M.N.B. or Belgian National Movement). Camille Joset becomes its national leader. This movement will undertake various resistance actions in the course of the war.
-
29-12-1940: President Roosevelt delivers his ‘arsenal of democracy’ speech.
-
31-12-1940: At the close of 1940, the secret trips by the Shetland Bus begin, a connection between the Shetland islands and Norway to transfer agents and weapons.
-
31-12-1940: The anti-Semitic movie Jud Süss is produced. The anti-Semitic movie Die Rothschildts is also widely shown.